- Plakalı heat exchangers fundamentally consist of two inlet ports, channelled heat transfer plates, and two outlet ports. Two of these inlet and outlet ports are for the heating fluid, and the other two are for the fluid to be heated. It is also possible to make exchangers with multiple heating or heated fluids through special production.
- The function of the plates inside the Plate Heat Exchanger is to provide heat transfer from the heating fluid to the fluid to be heated without mixing the fluids. The channelled structure of these plates allows the fluid to move in a highly turbulent manner. This turbulence leads to a more homogeneous distribution of heat in the fluid, resulting in a more efficient heat transfer.
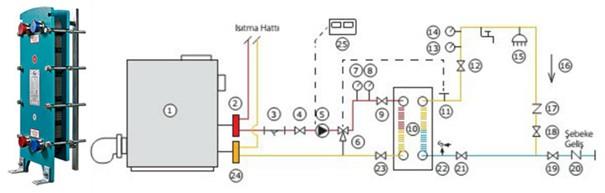
Plate heat exchangers are critical components commonly used in industrial applications to increase efficiency and provide energy savings. These exchangers designed to meet the needs of heat transfer are widely preferred in various sectors, especially in the chemical, food processing, and HVAC systems. This article provides detailed information on the working principles, structural features, and application areas of plate heat exchangers.
Structural Features
Plate heat exchangers are characterized by a series of channels created by bringing together thin metal plates. These plates are generally made of high heat-conducting materials such as stainless steel or titanium. The narrow channels between the plates are where the hot and cold fluids pass very close to each other, providing maximum heat transfer. The surfaces of the plates are often shaped with special patterns to ensure high heat transfer efficiency.
Working Principle
The basic working principle of plate heat exchangers is the movement of two different temperature fluids in opposite directions between the plates. These fluids are directed to create separate channels on both sides of the plates. While the hot fluid passes through one side of the plates, the cold fluid moves in the opposite direction. This counterflow arrangement ensures more efficient heat transfer.
Heat is transferred from the hotter fluid to the plates and then to the colder fluid. This process results in the temperatures of the fluids converging; as the hot fluid cools down, the cold fluid heats up.
Application Areas
Plate heat exchangers are ideal for applications that require space and energy savings. These include;
Chemical Industry: Cooling of reactors, heating of solutions, etc.
Food Processing: Sterilization processes such as milk pasteurization, fruit juice heating.
HVAC Systems: Meeting the heating, cooling, and hot water needs of buildings.
Energy Production: Waste heat recovery systems, combined cycle power plants.
Plate heat exchangers are essential components in modern industries for optimizing energy efficiency and operating costs. With high heat transfer efficiency, compact structures, and flexible application areas, these systems are an important part of sustainable technologies. With advancing technology, the designs and materials of plate heat exchangers are constantly being improved, making them even more suitable for industrial applications.